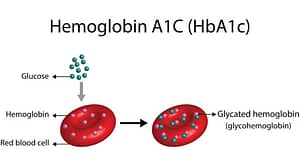
How To Reduce HbA1c Level Naturally?
Contrary to common belief, there are different ways to lower A1C. There are certain ways Exercise and Style Tips To Lower A1C Levels Include:
Engage In Physical activity: Exercising is one of the most important ways to lower A1c. Current guidelines recommend that adults use 150-300 principal minutes of moderate exercise every week. Individuals who take insulin should speak to their doctor about an appropriate pack.
Monitor Blood Glucose: This is vital to ensure that the person is achieving their goals and making necessary changes.
Track Progress: This is useful for self-motivation, monitoring change, and identifying the strategies that work for a person.
Involve Others: Lifestyle Change is often easier to adapt when other people can encourage and monitor progress.
Follow Nutrition tips: Monitoring of Carbohydrates can help a person control their blood sugar. General diet tips to lower A1C naturally include:
- Pay attention to the portion sizes
- Eat regularly, every 3 to 5 hours
- Eat similarly small portions with meals and snacks
- Plan meals in advance
- Keep a nutrition, medication, and exercise diary
- Spread high-carbohydrate foods throughout the day
- Ask a nutritionist for help
A doctor will advise each person differently on their dietary needs, including the number of carbohydrates they consume—this will depend on individual factors, including their training level and treatment plan.
Avoid Sugary Foods
One of the most important ways to lower A1C is avoiding sugary foods. Foods that take long time to suggest, like whole grains, have a slower and less impact on blood sugar levels. A person will digest simple sugars faster- found in candy and white bread . This can cause blood sugar to rise. Frequent increases in blood sugar can accelerate the development of diabetes and increase the risk of complications.So, try to cut down sugary foods to lower A1C naturally for an appropriate HbA1c reduce diet.
Limit Carbohydrates
How to reduce HbA1c level involves cuttting off carbs. A person with diabetes needs to control their carbohydrate intake, but they do not need to cut out carbohydrates altogether. A good HbA1c reduce diet should have very limited, planned carbohydrate.
What Does High or Low HbA1c Level Indicate?
High and low HbA1c levels provide valuable information about a person’s blood sugar control, especially for individuals with diabetes:
High HbA1c (Hyperglycemia): Elevated HbA1c levels (usually above 6.5% for diabetes diagnosis) indicate that a person’s average blood sugar levels have been consistently high over the past two to three months. This suggests poor blood sugar control, which can lead to various health complications over time. It may signal a need for adjustments in diabetes management, such as changes in medication, diet, or lifestyle. Uncontrolled hyperglycemia can increase the risk of heart disease, kidney damage, nerve problems, and vision issues.
Low HbA1c (Hypoglycaemia): Extremely low HbA1c levels may indicate that a person is experiencing frequent episodes of low blood sugar (hypoglycaemia). While this may seem beneficial at first glance, excessively low blood sugar can be dangerous and lead to symptoms like dizziness, confusion, and, in severe cases, loss of consciousness. It may suggest overly aggressive diabetes treatment, and healthcare providers might need to modify medication or insulin dosages to reduce the risk of hypoglycaemia.
HbA1c levels serve as a crucial indicator of long-term blood sugar control. High levels suggest a need for better management to prevent complications associated with hyperglycaemia, while very low levels may necessitate adjustments to avoid the risks of hypoglycaemia. Achieving a target HbA1c level is an essential goal in diabetes care to maintain good overall health.
How Fast Can HbA1c Level Lowered?
Lowering HbA1c levels can significantly improve overall health, especially for individuals with diabetes. Lower HbA1c can be achieved through natural methods or, in some cases, with the help of medications, though natural methods are preferred as they often yield better long-term results.
One can lower HbA1c within 3 months, whereas for some people, it might take years. It completely depends upon an individual, and more factors like age, immunity, technique chosen, treatment and management plans, diet, exercise, lifestyle, etc.
When Should The Blood Sugar Level Be Lowered?
In most cases, high blood sugar is detected at the time of the blood test result.
Blood sugar should be controlled as soon as it is over 1.10 g/L on an empty stomach. Initially, we will implement food hygiene measures – food balance and physical activity – and monthly monitoring as long as the parameters are not normalized.
Also, family tendencies or the presence of risk factors enhance vigilance. It is essential to control blood sugar when there are risk factors, such as being overweight, a genetic predisposition to diabetes high cholesterol level or triglyceride levels, or a history of cardiovascular disease.

Why reduce levels?
Many studies have shown that lowering A1C levels can help slow the progression of diabetes and reduce the risk of complications — such as nerve damage and cardiovascular disease — in both type 1 and type 2 diabetes.
When it comes to an A1C target range, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Many factors, including the type of diabetes and general health, can impact an A1C goal. A person can discuss a suitable target with their diabetes healthcare team.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) notes that the goal for most adults living with diabetes is an A1C of less than 7%. Many strategies, such as physical activity, diet, and medication, can help manage blood glucose levels and, therefore, also A1C levels.
Lifestyle tips
Exercise and lifestyle tips to help lower HbA1C levels include:
- Physical activity: Current guidelines recommend that adults perform a minimum of 150 minutes of moderate physical exercise each week. People who use insulin or have special considerations should contact their doctor about a suitable exercise plan.
- Routine activities: Housework, gardening, and other routine activities can all help keep a person moving.
- Monitoring blood glucose: This is crucial to ensure a person meets their targets and makes any necessary changes.
- Following the treatment plan: This includes the use of medications and lifestyle therapies.
- Weight management: The person may consider working with a healthcare professional to set realistic and achievable weight loss goals.
- Tracking progress: This is useful for self-motivation, monitoring changes, and identifying which strategies work for a person.
- Getting others involved: Lifestyle changes are often easier to adopt if other people can encourage and monitor progress.
Dietary tips
Everyone, especially people with diabetes, can benefit from a healthful diet that includes plenty of fresh fruit and vegetables and whole foods and is low in sugar, salt, and fat.
Monitoring carbohydrate intake can help a person manage their glucose levels.
General diet tips to lower A1C levels include:
- being mindful of portion sizes
- eating regularly, every 3–5 hours
- eating similar-sized portions at meals and snacks
- planning meals ahead of time
- keeping a journal of food, medication, and exercise
- spreading out carbohydrate-rich foods throughout the day
- choosing less-processed or whole foods such as whole grains, fruits, vegetables, legumes, and nuts
- eating a balanced diet complete with healthy proteins, fats, and carbohydrates
- seeking out the help of a registered dietitian
A healthcare professional will advise each person on their dietary needs, including the number of carbs they should consume. This will depend on individual factors, including the person’s exercise levels and treatment plan.
Nutrition
Nutrition plays an essential role in managing blood sugar levels. Following a suitable eating plan can help a person keep their blood sugar and A1C levels in a healthy range.
Creating a meal plan can be a useful tool to help a person manage their blood sugar. A dietitian can also help with recommending an eating plan. Additionally, people can try following the ADA’s Diabetes Plate Method.
For people living with diabetes, some important trends to incorporate into an eating plan include:
- eating sufficient fruits and vegetables-Consuming fresh Fruits, vegetables, and low-fat-containing dairy products contain less processed sugar, which is healthier than refined sugar. All fruits and whole vegetables contain natural sugars, but they also tend to be high in other nutrients, including fiber.
- eating lean protein
- choosing foods with less added sugar-one important way is to eliminate refined sugars. Refined sugars such as candy are quickly absorbed by the body, leading to dangerous blood sugar spikes. Consuming fresh Fruits, vegetables, and low-fat-containing dairy products contain less processed sugar, which is healthier than refined sugar. All fruits and whole vegetables contain natural sugars, but they also tend to be high in other nutrients, including fiber.Blood sugar is the level of sugar in the blood. It varies during the day but should be around 1g / L overall for an average rate. Eating meals and physical activity will make it evolve.
- limiting trans fats
- eating fewer processed foods
Setting HbA1C goals
As many factors can affect a suitable A1C range, there is no standardized approach when it comes to setting A1C goals. A diabetes healthcare team can help provide an individual with a target level that accounts for various factors, including the current A1C value and the date of the next test.
If the test result is already within a healthy range, the goal should be to maintain that. However, if a person enters the higher ranges, a doctor can suggest changes to their goals and treatment plans. They can help the person determine a reasonable target and the best strategy to achieve that goal.
Target levels in people with diabetes
A doctor will set a person’s target A1C level based on many factors. The right target varies from person to person.
For someone with diabetes, the target A1C level may depend on:
- the person’s age
- their overall health
- whether they are pregnant
- how long they have had diabetes
- their prescribed treatment plan
- any history of adverse effects from the treatment, including episodes of low blood glucose, or hypoglycemia
- any complications from diabetes
- the person’s preferences and treatment priorities
In general, a doctor might recommend aiming for A1C levels under 6.5% if a person:
- is young and has a long life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a short period
- is effectively managing their diabetes with lifestyle changes or metformin alone
- is otherwise in good health
A doctor might recommend A1C targets of 7.0–8.5% if a person:
- is older and has a shorter life expectancy
- has had diabetes for a longer period
- has diabetes that is hard to manage, even with multiple medications
- has a history of severe hypoglycemia or other adverse effects of treatment
- has experienced complications of diabetes
- has other chronic health conditions
People can work with their doctor to reassess and adjust their A1C targets over time. The condition and treatment goals may change.
HbA1C levels by age
Age is one of many factors that affect a person’s blood glucose levels. However, while advancing age is associated with increased blood glucose levels, the changes are often small.
Research from 2019 defined age-related A1C percentage levels in healthy populations as:
How often to get the A1C test
To screen for diabetes, a doctor may order an A1C test for someone over 45 years. They may also do this for younger people who have other risk factors.
After diagnosing diabetes, a doctor determines how often to test A1C levels.
If a person meets their treatment goals, they may need an A1C test twice a year. When managing blood glucose levels is challenging, a person needs this test more frequently.
Summary
A doctor orders an A1C test to check whether someone has prediabetes or type 1 or 2 diabetes. Doctors also use this test to monitor blood glucose levels in people with diabetes to check how well their treatment plan is working.
HbA1C test results are usually a percentage but may come as an eAG measurement. Target HbA1C levels vary from person to person, depending on age, overall health, and other factors.
Having high HbA1C levels may indicate a person has diabetes or a high risk of related complications. In this case, a doctor will work with the individual to adjust the treatment approach.