One of the first known uses of a medical robot dates back to the 1980s, when the “PUMA 560”, which was not originally designed for medical use, was adapted by scientists at the University of British Columbia to assist in conducting brain biopsies.
Since then, the field of medical robots has produced a number of sophisticated designs that aim to help healthcare professionals conduct a wide range of tasks, from surgery to diagnostics and rehabilitation. These medical robots, often equipped with state-of-the-art sensors, actuators, and artificial intelligence algorithms, enhance the accuracy and efficiency of medical procedures.
Despite initial unease with the idea of a robot handling surgeries or providing emotional support, they are increasingly prevalent in healthcare. Engineers have compelling reasons to develop medical robots. Unlike humans, these tireless machines with steady ‘hands’ can execute precise movements beyond human range, providing prolonged patient support. They excel in automating lower-level tasks, allowing professionals to focus on high-level work. This post considers five robots currently utilized in hospitals and treatment centers to improve care and patient outcomes.
Here we will explore the benefits of medical robotics, highlighting the impact these technologies have had on the healthcare industry.
Enhancing Precision and Accuracy in Surgical Procedures
The integration of medical robots with advanced imaging technologies has revolutionized surgical procedures by providing surgeons with real-time, highly detailed visuals of the area being operated on. These robots are designed with superior mechanical stability and precise control mechanisms, significantly improving the guidance, stabilization, and movement control during surgeries. This advancement not only minimizes the risk of human error but also elevates the overall precision of surgical operations.
Moreover, the incorporation of haptic feedback systems in certain medical robots has been a groundbreaking development. These systems allow surgeons to ‘feel’ the characteristics of the tissues they are operating on, even though they are manipulating instruments remotely. This capability facilitates surgeries to be performed with an unprecedented level of sensitivity and precision, further enhancing the effectiveness and safety of medical procedures.
Improving Surgical Outcomes and Recovery Times
By enhancing the precision of surgical techniques and minimizing invasiveness, medical robots significantly improve surgical outcomes and accelerate recovery times.3 The precise control and ability to navigate through smaller incisions reduce trauma to surrounding tissues and lower the risk of complications, thereby shortening recovery periods.
Specialized Healthcare Services
Medical robots are revolutionizing access to specialized healthcare by enabling remote consultations and procedures. They support teleoperated systems, allowing surgeons to perform surgeries remotely.This breakthrough means that geographical barriers no longer prevent patients from accessing world-class experts, regardless of where they live.
In the past, geographical barriers meant that patients in remote or underserved areas often faced significant challenges in accessing specialist care. Now, thanks to medical robotics, these individuals can receive treatment from top specialists around the globe, overcoming the limitations set by traditional healthcare delivery methods.
Mitigating Surgeon Fatigue and Improving Ergonomic Conditions
Recent research analyzing the sleep patterns and mental fatigue of surgical residents highlighted a concerning trend: they experience fatigue during nearly half (48 %) of their waking hours. The study also found that their fatigue levels were predicted to increase the risk of medical error by 22 %.
Medical robots have emerged as a solution to combat surgeon fatigue and ergonomic challenges. By taking on physically demanding tasks—such as automating repetitive movements and stabilizing surgical instruments—these robots significantly reduce the physical strain on surgeons. This reduction in strain is crucial in minimizing the risk of fatigue-induced errors during surgeries.
Advancements in Robotic-Assisted Rehabilitation and Therapy
Major advancements in robotic-assisted rehabilitation and therapy have included the development of exoskeletons and wearables that facilitate the recovery of movement via targeted assistance feedback, robotic platforms equipped with virtual reality interfaces for immersive rehabilitation, and the integration of AI to develop adaptive and responsive therapies tailored to the individual patient.
Here are five robots currently being implemented in hospitals and treatment centers to improve quality of care and patient outcomes.
1. The da Vinci® Surgical Robot
It is unthinkable, but true: More than 250,000 people die in the U.S. each year from medical errors, some of which are likely preventable.While this is a broad category encompassing a range of different problems, it’s certainly true that the more control surgeons have in their operations, the better. The da Vinci Surgical System, a multi-armed wonderbot, is being used to reduce surgical errors and make surgery less invasive for thousands of patients.
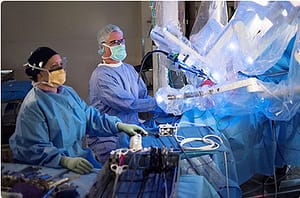
The da Vinci Surgical System gives surgeons more precise control for a range of procedures. Using magnified 3D high-definition vision and controls that strap to a surgeon’s wrists and hands, the da Vinci System makes tiny, exact incisions that human hands might not otherwise be able to make. This offers enhanced control to surgeons and, since the surgery is less invasive than traditional surgery, a faster healing time for patients.
2. The Xenex Germ-Zapping Robot
Along with minimizing medical and surgical errors, hospital-acquired infections (HAIs) are another widespread problem in healthcare that could be improved with robots.
HAIs often occur because hospitals can’t always clean rooms with 100 percent sterility between patients, whether due to time constraints or the simple invisibility of germs. Whatever the reason, patients who are already immunocompromised are more susceptible to bacterial infection.

To combat this elemental problem, the Xenex, an automated and portable robot, is used to disinfect entire hospital rooms in minutes using pulsed, full-spectrum UV rays that kill a range of infectious bacteria. It’s designed to reduce HAIs such as Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) by killing the microorganisms that cause them, which can be particularly resistant to treatment. Plus, the robot is kind of cute—it looks like an R2-D2 designed to save lives.
3. The PARO Therapeutic Robot
Unlike the first two robots, this one is not designed to save lives per se, but to improve quality of life during recovery from surgery or treatment for depression or other mental illness. The PARO Therapeutic Robot is an interactive device that looks like a baby harbor seal and is designed to provide the benefits of animal therapy without relying on live animals. Animal therapy is a common tool for easing patient stress, but there are not always trained animals available to satisfy current needs. Friendly, animal-like PARO fits the bill.

PARO is used extensively with elderly patients with dementia, and has been proven to reduce stress and provide comfort to anxious patients.The fuzzy PARO can respond to its name, enjoys being stroked, and, over time, develops a customized, pleasing personality tailored by its memory of previous interactions. PARO also naps, blinks, wiggles its flippers and makes funny little noises, especially for its owner. Bonus: it charges by “sucking” on a charger shaped like a pacifie.
4. The CyberKnife
The Cyberknife is a robotic surgery system that delivers radiation therapy to tumors with sub-millimeter precision.5 Invented in the 1990s, the CyberKnife system is now being used to treat cancer at hospitals and treatment centers all over the U.S. Not a knife per se, the system is a radiation source mounted on a robot, which allows for a targeted beam of radiotherapy that maneuvers and adapts quickly. It can deliver radiation to a tumor (malignant or benign), repositioning itself at many minutely different angles to target the tumor from all sides without having to reposition the patient.
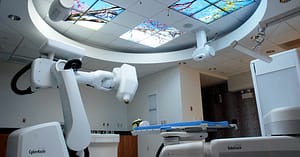
The CyberKnife has allowed for treatment of tumors in areas of the body that were once surgically complex to operate on, including the prostate, head, neck and liver. This “surgery” is actually non-invasive and minimizes the exposure of healthy organs and tissues to radiation. What’s more, the CyberKnife has been shown to be remarkably effective in the long term for prostate cancer, although long-term control of other cancers have not been studied.
5. The TUG Robot
You may never think about it, but transporting supplies, meals and other materials around the hospital is a drag on efficiency. One estimate shows that a typical 200-bed hospital moves meals, linens, lab samples, waste and other items the equivalent of 53 miles per day. Enter TUG, an autonomous mobile robot developed by Aethon Inc. to ferry supplies to where they are needed, freeing employees from heavy physical loads and allowing them to focus on patient care.

When the University of California, San Francisco Medical Center at Mission Bay opened in 2015, it rolled out 25 TUG robots to improve their transportation operations.8 They are programmed with the hospital’s floor plan and are also equipped with a variety of sensors to ensure they don’t run into anything on their way to the lab. They also kindly ask people to stand aside as they move into congested hallways.
Future Outlook
A whole world of innovation is possible as robots become more sophisticated and responsive and make greater inroads into medical treatment. HAIs, medical errors, cancer and mental illness have long been viewed as intractable problems in healthcare, but biomedical engineering is helping to find new ways forward.
The future of medical robots holds much promise for the development and improvement of healthcare systems across the globe. In the near future, as AI and machine learning technologies become increasingly integrated into medical robotics, we can expect to see notable enhancements in surgical accuracy, expanded telemedicine options, and superior patient outcomes.
Moreover, a shift toward the miniaturization and enhanced portability of medical robots is projected. This evolution aims to further democratize access to specialized healthcare services, making high-quality care more accessible to diverse populations worldwide.