Debunking the Male Menopause Myth
The term “male menopause” has been used to describe decreasing testosterone levels related to aging. But aging-related hormone changes in women and men are different.
In women, ovulation ends and hormone production plummets during a relatively short period of time. This is known as menopause. In men, production of testosterone and other hormones declines over a period of many years and the consequences aren’t necessarily clear. This gradual decline of testosterone levels is called late-onset hypogonadism or age-related low testosterone.
Recognizing low testosterone levels
A man’s testosterone levels decline on average about 1% a year after age 40. But most older men still have testosterone levels within the normal range, with only an estimated 10% to 25% having levels considered to be low.

Low testosterone levels in older men often go unnoticed. Testosterone levels can be checked by a blood test, but tests aren’t routinely done. And many men who have low testosterone levels experience no symptoms. In addition, the signs and symptoms associated with low testosterone aren’t specific to low testosterone. They can also be caused by a person’s age, medication use or other conditions, such as having a body mass index of 30 or higher. Still, signs and symptoms suggestive of low testosterone include followings:
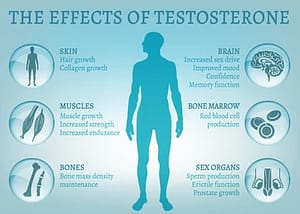
Symptoms Of Andropause
Andropause is a gradual process that can span over several years. It typically starts in the late 40s or early 50s and can continue into the 60s or 70s. The symptoms of andropause are often subtle and can be mistaken for normal signs of ageing. However, it is essential to recognize these symptoms as they can significantly impact a man’s quality of life. Some common symptoms of andropause include: Male menopause can cause physical, sexual, and psychological problems. They typically worsen as you get older. They can include:
- low energy
- depression or sadness
- decreased motivation
- lowered self-confidence
- difficulty concentrating
- insomnia or difficulty sleeping
- increased body fat
- reduced muscle mass and feelings of physical weakness
- gynecomastia, or development of breasts
- decreased bone density
- erectile dysfunction
- reduced libido
- infertility
You may also experience swollen or tender breasts, decreased testicle size, loss of body hair, or hot flashes. Low levels of testosterone associated with male menopause have also been linked to osteoporosis. This is a condition where your bones become weak and brittle. These are rare symptoms.
Changes in Testosterone Over the Years
Before you hit puberty, your testosterone levels are low. Then they increase as you sexually mature. Testosterone is the hormone that fuels typical changes involved in male puberty, such as:
- growth of your muscle mass
- growth of your body hair
- lowering of your voice
- changes in your sexual functioning.
As you age, your testosterone levels will typically begin to drop. According to the Mayo Clinic, testosterone levels tend to decline an average of 1 percent per year after a males turn 30. Some health conditions can cause earlier or more drastic declines in your testosterone levels.
Causes of Andropause:
The primary cause of andropause is the natural decline in testosterone levels as men age. However, other underlying health conditions can contribute to this decline. Some of the most common causes of andropause include:
Chronic illness: Certain health conditions such as diabetes, obesity, and chronic liver or kidney disease can affect hormone production and lead to andropause.
Medications: Some medications used to treat prostate cancer, depression, and high blood pressure can interfere with testosterone production and cause symptoms of andropause.
Lifestyle factors: Poor diet, lack of exercise, excessive alcohol consumption, and smoking can all contribute to the decline in testosterone levels and increase the risk of andropause.
Treatments for Andropause:
The good news is that there are several effective treatments available for andropause that can help manage its symptoms and improve overall well-being. Here are some common treatments for male menopause:
Testosterone replacement therapy (TRT): This is the most common treatment for andropause, where synthetic testosterone is administered through injections, gels, patches, or pellets. This helps to stabilize hormone levels and alleviate symptoms such as low libido, fatigue, and mood changes. However, it’s very controversial. Like performance-enhancing steroids, synthetic testosterone can have damaging side effects. For example, if you have prostate cancer, it may cause your cancer cells to grow. If your doctor suggests hormone replacement therapy, weigh all of the positives and negatives before making your decision.
Lifestyle modifications: Making healthy lifestyle changes such as regular exercise, eating a balanced diet, reducing alcohol consumption, and quitting smoking can help manage symptoms of andropause and improve overall health.
The most common type of treatment for symptoms of male menopause is making healthier lifestyle choices. For example, your doctor might advise you to:
- eat a healthy diet
- get regular exercise
- get enough sleep
- reduce your stress
These lifestyle habits can benefit all men. After adopting these habits, MAABs who are experiencing symptoms of male menopause may see a dramatic change in their overall health.
Counselling: Andropause can have a significant impact on a man’s emotional well-being. Seeking counselling or therapy can help men cope with the changes they are experiencing and manage any mood changes or depression.
Medications: In some cases, medications such as antidepressants or medications used to treat erectile dysfunction may be prescribed to manage specific symptoms of andropause.
Outlook
It’s normal to experience a decline in your testosterone levels as you get older. For many men, the symptoms are manageable, even without treatment. It is essential to note that every man’s experience with andropause is different. Some may only experience mild symptoms, while others may experience more severe symptoms that significantly impact their daily lives. It is crucial to consult a healthcare professional for proper diagnosis and treatment.





